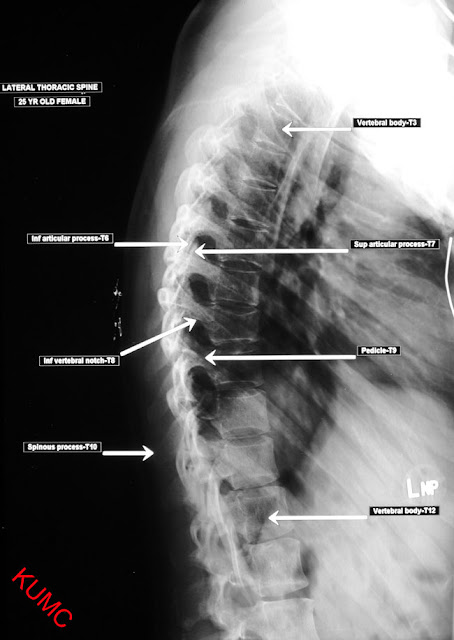
The chest x-ray is the most commonly performed diagnostic x-ray examination. A chest x-ray makes images of the heart,lungs, airways, blood vessels and the bones of the spine and chest.
anatomy of chest
PA PROJECTION : CHEST
Pathology Demonstrated:
-pleural effusions
-pneumothorax
-atelectasis
-signs of infection
Technical Factors:
-IR size 35x43 cm (14x17 inches)
-moving or stationary grid
-110-125 kV range
-mAs 3-4
Shielding :
-lead shielding around the waist or adjustable mobile
shield on a stand behind the patient
Patient position:
-patient in erect , feet spreed slighty , weight
distributed equally on both feet
-chin raised , resting against IR
-hands on lower hips , palms out elbow partially
flexed
-shouders rotated forward against IR to allow scapulae
to move
Laterally clear of lung fields. Shoulders depressed
downward to move clavicle below the apices
Part position
-alig midsaggital plane with CR and to midline of IR
with equal
Margins between lateral thorax and sides of IR
-Ensure no rotation to thorax
-raise or lower CR and IR as needed to the level of T7
for average patient.
(top of IR will be 1.5 to 2 inches ,or 4 to 5 cm ,
above shouders on ost average patient.)
Central Ray
-CR perpendicular to IR and centered to midsaggital
plane at level of T7 (7 to 8 inches or 18 to 20 cm ,below vertebra prominens or
to inferior angel of scapula)
-IR centered to CR
-SID of 72 inches (180 cm)
Collimation
-collimate on four sides to area of lung field.(top
borders of illuminated field should be to level of vertebra prominens and
lateral borders to outer skin margins.)
Respiration
-exposure made at end of second full inspiration
radiographic image of chest X-Ray
video of Chest radiograph positioning
for more info click right HERE